Introduction
Features
- Embedded payment: generate card payment form in your payment page and let GrubPay handle the rest
- Redirected payment: be redirected to GrubPay page to create a transaction
- Direct payment: create a transaction with one api call (PCI compliance required)
Before Integration
Before integration, merchants need to sign a contract with GrubPay and get the merchant ID, merchant key and login name.
Terminologies and Concepts
Important
This document will refer to the following terms. Developers should familiarize themselves with these terms.
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Merchant | A merchant onboard GrubPay |
| Customer | A customer of a merchant of GrubPay (usually a buyer) |
| JS SDK | A JS software library developed by GrubPay for merchants using their own payment page |
| Redirected Integration | Protocol for merchants using GrubPay's payment page |
| Embedded Integration | Protocol for merchants using their own payment page via JS SDK |
| Auth API | GrubPay's universal api for tokenizing cards and creating transactions |
| Token | Token representation of a customer card, can be used repeatedly for future API calls |
| Tokenize | Making a request to Auth API for a token |
| Purchase | Making a request to Auth API to create a transaction |
| Capture | Approve a transaction to proceed forward to settlement |
secureId | A session identifier for Embedded integration protocol |
| ACH | An Automated Clearing House bank transfer is an electronic payment made between banks, requiring sender's account information |
Request / Response format
All request and response are in JSON format. It should not be treated as fixed or as a schema, new fields may be added as the API evolves, and the order of fields may change. Your applications must therefore be resilient to the reordering of fields within a JSON object.
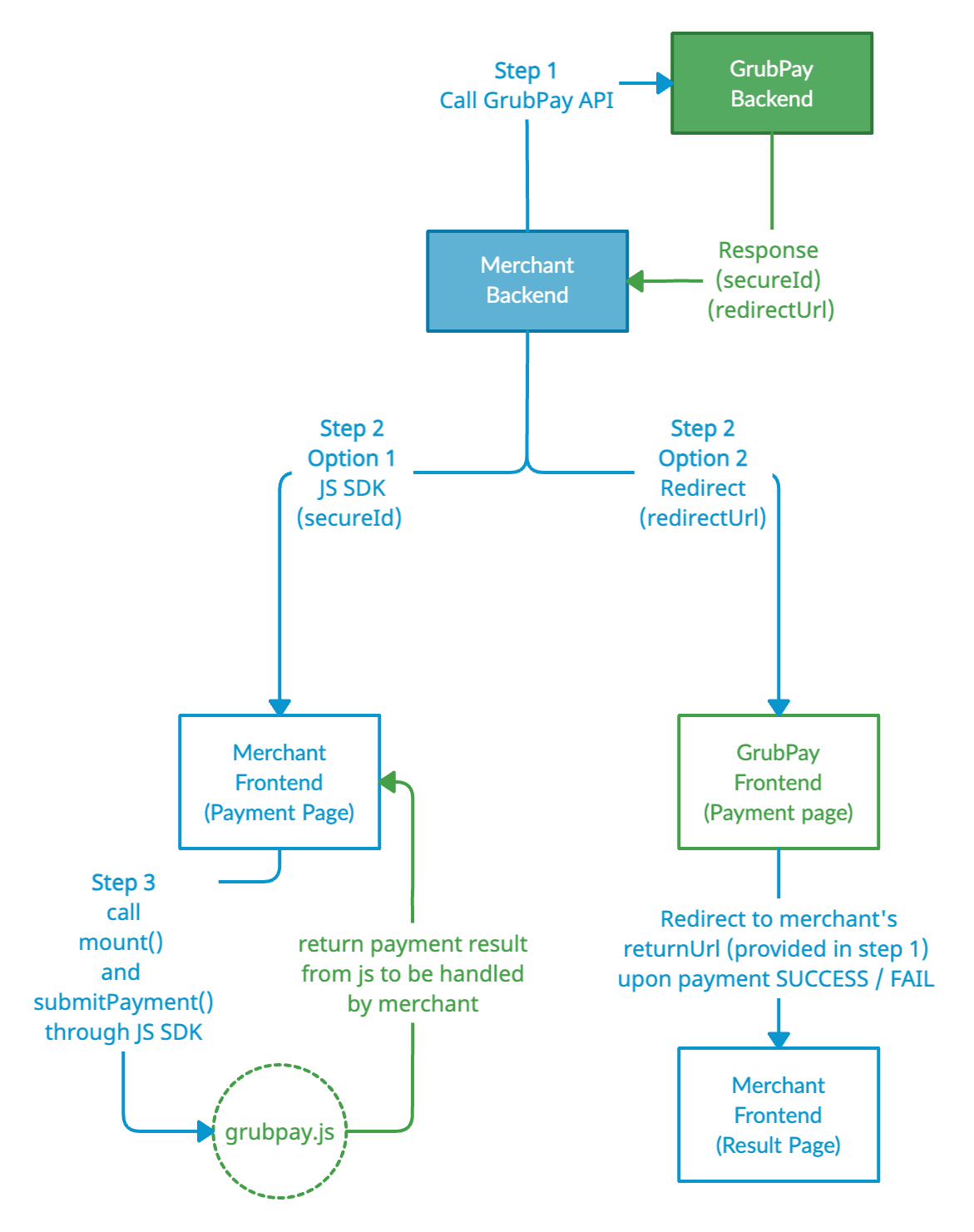
Integration Workflow
The flow is slightly different for the two methods, but it all starts with calling Auth API from the backend.